Information of ICE
| ICEberg ID | 231_CIME |
|---|---|
| ICE Name | CIMEL3catR3 |
| ICEO ID | - |
| Organism | Streptococcus thermophilus LMG18311 |
| Size | - |
| GC Content (%) | - |
| Insertion site | fda |
| Function | - |
| Species that ICE can be transferred to | Streptococcus thermophilus CNRZ385 |
| Nucleotide Sequence | - |
| Coordinates | - |
| Putative oriT region | - |
| Putative relaxase | - |
Function tags R Antibiotic resistance V Virulence factor M Metal resistance D Defense system G Degradation S Symbiosis
The Interaction Network among ICE/IME/CIME
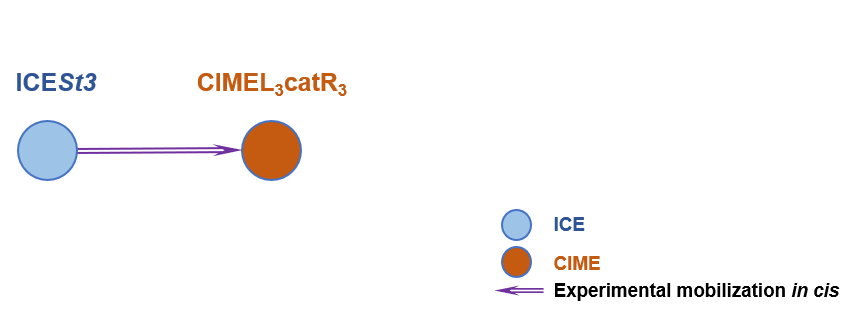
Detailed Informatioin of the Interaction Network
| # | ICE | Inter_Ele [Type] | Methods | Donors | Recipients | Exper_Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CIMEL3catR3 | ICESt3 [ICE] | | Streptococcus thermophilus | Streptococcus thermophilus | 21722203 |
| (1) Chapleau M, Guertin JF, Farrokhi A, Lerat S, Burrus V, Beaulieu C. (2016) Identification of genetic and environmental factors stimulating excision from Streptomyces scabiei chromosome of the toxicogenic region responsible for pathogenicity. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 May;17(4):501-9. [PubMed:26177341] |
| (2) Bellanger X, Morel C, Gonot F, Puymege A, Decaris B, Guédon G. (2011) Site-specific accretion of an integrative conjugative element together with a related genomic island leads to cis mobilization and gene capture. Mol Microbiol. 2011 Aug;81(4):912-25. [PubMed:21722203] |
| (3) Zhang Y, Loria R. (2017) Emergence of Novel Pathogenic Streptomyces Species by Site-Specific Accretion and cis-Mobilization of Pathogenicity Islands. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2017 Jan;30(1):72-82. [PubMed:27977935] |